
The reflection of triangle will look like this. Point is units from the line so we go units to the right and we end up with. Is units away so we’re going to move units horizontally and we get. Point is units from the line, so we’re going units to the right of it. We’re just going to treat it like we are doing reflecting over the -axis. Graphically, this is the same as reflecting over the -axis. This line is called because anywhere on this line and it doesn’t matter what the value is.


A line rather than the -axis or the -axis. For example, when point P with coordinates (5,4) is reflecting across the X axis and mapped onto point P’, the coordinates of P’ are (5,-4). Let’s say we want to reflect this triangle over this line. What is the rule for a reflection across the X axis The rule for reflecting over the X axis is to negate the value of the y-coordinate of each point, but leave the x-value the same.
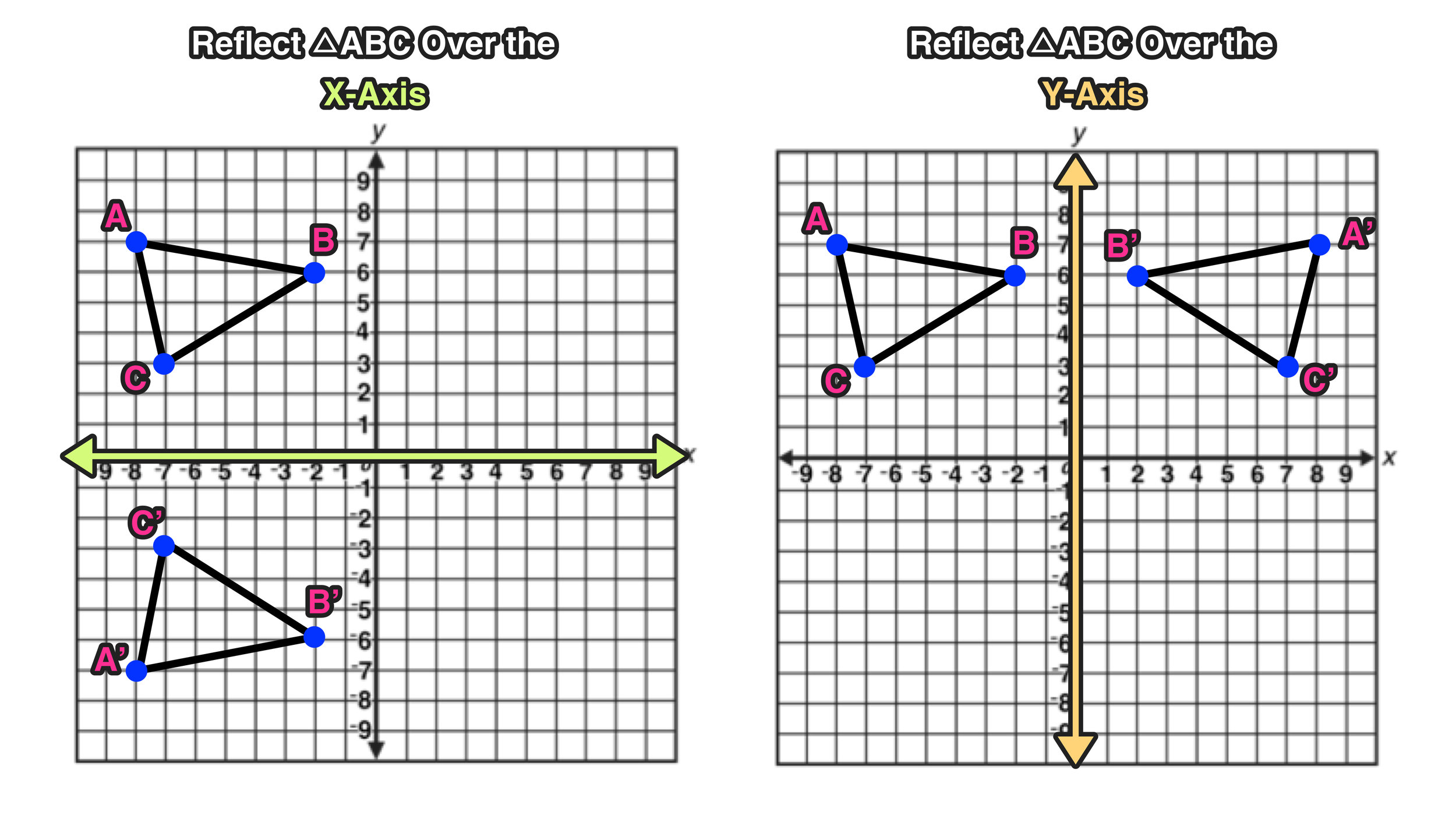
In this case to reflex over x 1 we shift x x + 1, reflect 1 x and shift back 2 x. The procedure to determine the coordinate points of the image are the same as that of the previous example with minor differences that the change will be applied to the y-value and the x-value stays the same. To reflect over a vertical line, such as x a, first translate so the line is shifted to the y-axis, then reflect over it, then translate back so the line is shifted to its original position. In the end, we found out that after a reflection over the line x=-3, the coordinate points of the image are:Ī'(0,1), B'(-1,5), and C'(-1, 2) Vertical Reflection The y-value will not be changing, so the coordinate point for point A’ would be (0, 1) Since point A is located three units from the line of reflection, we would find the point three units from the line of reflection from the other side. Similarly, you may ask, what is the rule for a reflection across the X axis When you reflect a point across the line y x, the x-coordinate and y-coordinate change places. the angle of incidence i the angle of reflection r. The rule for reflecting over the X axis is to negate the value of the y-coordinate of each point, but leave the x-value the same. the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal to the surface of the mirror all lie in the same plane. Subsequently, question is, what are the two rules of reflection The Laws of Reflection state. A reflection over the x-axis can be seen in the picture below in which point A is reflected to its image A'. We’ll be using the absolute value to determine the distance. The rule for a reflection over the x -axis is (x,y) (x,y). Since it will be a horizontal reflection, where the reflection is over x=-3, we first need to determine the distance of the x-value of point A to the line of reflection. This is a different form of the transformation. Since the line of reflection is no longer the x-axis or the y-axis, we cannot simply negate the x- or y-values. See Problem 1c) below.Let’s use triangle ABC with points A(-6,1), B(-5,5), and C(-5,2). The argument x of f( x) is replaced by − x. And every point that was on the left gets reflected to the right. Every point that was to the right of the origin gets reflected to the left. Reflection across the x-axis: y -f(x) Pick three points with x and y value and graph Pick three points and graph Divide y values by -1 while x values stay. Every y-value is the negative of the original f( x).įig. Its reflection about the x-axis is y = − f( x). Only the roots, −1 and 3, are invariant.Īgain, Fig. Thus, to reflect f(x) over x-axis, multiply f(x) by -1. To reflect a function over x-axis, we need to multiply the function by -1. Examine what happens to make the parent graphs reflect over the x-axis: linear: y -x. To reflect an equation over the x-axis, make the x values opposite outside of the symbol. And every point below the x-axis gets reflected above the x-axis. The function which represents the reflection over x-axis is the attached graph. These are both functions, each function has been reflected over the x-axis. Every point that was above the x-axis gets reflected to below the x-axis. The distance from the origin to ( a, b) is equal to the distance from the origin to (− a, − b).į( x) = x 2 − 2 x − 3 = ( x + 1)( x − 3).įig. If we reflect ( a, b) about the x-axis, then it is reflected to the fourth quadrant point ( a, − b).įinally, if we reflect ( a, b) through the origin, then it is reflected to the third quadrant point (− a, − b). It is reflected to the second quadrant point (− a, b). C ONSIDER THE FIRST QUADRANT point ( a, b), and let us reflect it about the y-axis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
